London (pronounced /ˈlʌndən/) is the capital of England and the United Kingdom. A major settlement for two millennia, its history goes back to its founding by the Romans, who called it Londinium. London's core, the ancient City of London, the 'square mile', retains its mediaeval boundaries. Since at least the nineteenth century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis developed around it. Today, the bulk of this conurbation forms the London region and the Greater London administrative area, with its own elected mayor and assembly.
London is a leading global city and one of the world's largest financial centres with the largest city GDP in Europe. Central London is home to the headquarters of most of the UK's top 100 listed companies (the FTSE 100) and more than 100 of Europe's 500 largest. London's influence in politics, finance, education, entertainment, media, fashion, the arts and culture in general contributes to its global position. It is a major tourist destination for both domestic and overseas visitors. London hosted the 1908 and 1948 Summer Olympics and will host the 2012 Summer Olympics. London contains four World Heritage Sites: the Tower of London; the historic settlement of Greenwich; the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; and the site comprising the Palace of Westminster, Westminster Abbey and St. Margaret's Church.
London has a diverse range of peoples, cultures, and religions, and more than 300 languages are spoken within its boundaries. In July 2007 it had an official population of 7,556,900 within the boundaries of Greater London, making it the most populous municipality in the European Union.[20] The Greater London Urban Area (the second largest in the EU) has a population of 8,278,251. while the metropolitan area (the largest in the EU) has an estimated total population of between 12 million and 14 million. The London Underground network, administered by Transport for London, is the most extensive underground railway network in the world, London Heathrow Airport is the world's busiest airport by number of international passengers and the airspace is the busiest of any urban centre in the world.
Governance
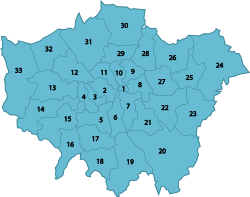
Local government
The administration of London is formed of two tiers—a city-wide, strategic tier and a local tier. City-wide administration is coordinated by the Greater London Authority (GLA), while local administration is carried out by 33 smaller authorities.[54] The GLA consists of two elected components; the Mayor of London, who has executive powers, and the London Assembly, who scrutinise the mayor's decisions and can accept or reject his budget proposals each year.
The headquarters of the GLA is City Hall, Southwark; the current mayor is Boris Johnson. The mayor's statutory planning strategy is published as the London Plan, which as of mid-2009 is being revised, for final publication in 2011. The local authorities are the councils of the 32 London boroughs and the City of London Corporation.[55] They are responsible for most local services, such as local planning, schools, social services, local roads and refuse collection. Certain functions, such as waste management, a provided through joint arrangements.
Policing in Greater London, with the exception of the City of London, is provided by the Metropolitan Police Service, overseen by the Metropolitan Police Authority. The City of London has its own police force – the City of London Police. The British Transport Police are responsible for police services on National Rail and London Underground services in the capital.
The London Fire Brigade is the statutory fire and rescue service for Greater London. It is run by the London Fire and Emergency Planning Authority and is the third-largest fire service in the world.[58] National Health Service ambulance services are provided by the London Ambulance Service NHS Trust, the largest free at the point of use emergency ambulance service in the world. Her Majesty's Coastguard and the Royal National Lifeboat Institution operate on the River Thames.
National government
London is an important city because the Government of the United Kingdom is located around the Palace of Westminster. Many government departments are located close to Parliament, particularly along Whitehall, including the Prime Minister's residence at 10 Downing Street.[62] The British Parliament is often referred to as the "Mother of Parliaments" (although this sobriquet was first applied to England itself by John Bright)[63] because it has been the model for most other parliamentary systems, and its Acts have created many other parliaments.
Geography
Scope
Greater London is the top-level administrative subdivision covering London. The small, ancient City of London at its core once contained the whole settlement, but as the urban area grew the City Corporation resisted attempts to amalgamate it with its suburbs, causing "London" to be defined in a number ways for different purposes; and the situation was once open to legal debate. Forty percent of Greater London is covered by the London postal district, within which 'LONDON' forms part of postal addresses.
The London telephone area code covers a larger area, similar in size to Greater London, although some outer districts are omitted and some places just outside are included. The area within the orbital M25 motorway is sometimes used to define the "London area" and the Greater London boundary has been aligned to it in places.
Outward urban expansion is now prevented by a metropolitan green belt, although the built-up area extends beyond the boundary in places, resulting in a separately-defined Greater London Urban Area. Beyond this is the vast London commuter belt. Greater London is split for some purposes into Inner London and Outer London. The city is split by the River Thames into North and South, with an informal Central London area in its interior. The coordinates of the nominal centre of London, traditionally considered to be the original Eleanor Cross at Charing Cross near the junction of Trafalgar Square and Whitehall, are approximately  51°30′29″N 00°07′29″W / 51.50806°N 0.12472°W / 51.50806; -0.12472.
51°30′29″N 00°07′29″W / 51.50806°N 0.12472°W / 51.50806; -0.12472.
Status
Within London, both the City of London and the City of Westminster have City status and both the City of London and the remainder of Greater London are the ceremonial counties.[73] The current area of Greater London has incorporated areas that were once part of the counties of Middlesex, Kent, Surrey, Essex and Hertfordshire. London's status as the capital of the England, and later the United Kingdom, has never been granted or confirmed officially—by statute or in written form.
Its position was formed through constitutional convention, making its status as de facto capital a part of the UK's unwritten constitution. The capital of England was moved to London from Winchester as the Palace of Westminster developed in the 12th and 13th centuries to become the permanent location of the royal court, and thus the political capital of the nation.[75] More recently, Greater London has been defined as a region of England and in this context known as London.
Topography
Greater London covers an area of 607 square miles (1,570 km2). Its primary geographical feature is the Thames, a navigable river which crosses the city from the south-west to the east. The Thames Valley is a floodplain surrounded by gently rolling hills including Parliament Hill, Addington Hills, and Primrose Hill. The Thames was once a much broader, shallower river with extensive marshlands; at high tide, its shores reached five times their present width.
Since the Victorian era it has been extensively embanked, and many of its London tributaries now flow underground. The Thames is a tidal river, and London is vulnerable to flooding. The threat has increased over time due to a slow but continuous rise in high water level by the slow 'tilting' of Britain (up in the north and down in the south) caused by post-glacial rebound.
In 1974, a decade of work began on the construction of the Thames Barrier across the Thames at Woolwich to deal with this threat. While the barrier is expected to function as designed until roughly 2070, concepts for its future enlargement or redesign are already being discussed.
Climate
London has a temperate marine climate (Koppen climate classification Cfb), like much of the British Isles, so the city rarely sees extremely high or low temperatures. Summers are warm with average high temperatures of 21 °C (70 °F) – 24 °C (75 °F) and lows of 11 °C (52 °F) – 14 °C (57 °F). But temperatures can exceed 25 °C (77 °F) on many days, and in almost every year they exceed 30 °C (86 °F) on some days. The highest temperature ever recorded was 39 °C (102 °F) on 10 August 2003.
Winters in London are chilly, but rarely below freezing with daytime highs around 8 °C (46 °F) – 12 °C (54 °F), while spring has mild days and cool evenings. The lowest ever recorded temperature in recent years was −10 °C (14.0 °F) on 10 January 1982. Autumn is usually mild but often unsettled as colder air from the north and warmer air from the south meet. London is a relatively dry city with regular but generally light precipitation throughout the year, with an average of 583.6 millimetres (22.98 in) every year.
Snow is relatively uncommon, particularly because heat from the urban area can make London up to 5 °C (9 °F) warmer than the surrounding areas in winter. Some snowfall, however, is usually seen up to a few times a year. The snowfall of February 2009 was the heaviest London had seen for 18 years.
| [hide]Weather data for London |
|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|
| Record high °C (°F) | 15
(59) | 16
(61) | 21
(70) | 26
(79) | 30
(86) | 33
(91) | 37
(99) | 39
(102) | 30
(86) | 26
(79) | 19
(66) | 15
(59) | 39
(102) |
|---|
| Average high °C (°F) | 8
(46) | 8
(47) | 11
(52) | 13
(56) | 17
(63) | 20
(68) | 23
(73) | 23
(73) | 19
(67) | 15
(59) | 11
(52) | 9
(48) | 16
(60) |
|---|
| Average low °C (°F) | 2
(36) | 2
(36) | 4
(39) | 5
(41) | 8
(46) | 11
(52) | 14
(57) | 13
(55) | 11
(52) | 8
(46) | 5
(41) | 3
(37) | 8
(46) |
|---|
| Record low °C (°F) | -10
(14) | -9
(16) | -8
(18) | -2
(28) | -1
(30) | 5
(41) | 7
(45) | 6
(43) | 3
(37) | -4
(25) | -5
(23) | -7
(19) | -10
(14) |
|---|
| Precipitation mm (inches) | 52
(2.05) | 34
(1.34) | 42
(1.65) | 45
(1.77) | 47
(1.85) | 53
(2.09) | 38
(1.5) | 47
(1.85) | 57
(2.24) | 61
(2.4) | 52
(2.05) | 54
(2.13) | 582
(22.91) |
|---|
| Sunshine hours | 62 | 57 | 124 | 150 | 186 | 210 | 186 | 186 | 150 | 93 | 60 | 31 | 1,495 |
|---|
| Avg. precipitation days | 17 | 13 | 15 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 15 | 165 |
|---|
| Source: Average high, low and precipitation from the Weather Channel [82] 2009-11-29 |
| Source #2: Record high and low are unsourced failed source verification on 2009-11-29 – may be vandalised |
London is in USDA Hardiness zone 9, and AHS Heat Zone 2. Although extreme weather does not happen very often, deep depressions have been known to pass through like the Great Storm of 1987. Tornados are rare, but the Kensal Green area of the city was hit by the 2006 London tornado causing £10 million of damage and injuring 6 people. In the second half of the 19th century and the first half of the 20th, London was noted for its dense fogs and smogs. Following the deadly Great Smog of 1952, the Clean Air Act 1956 was passed, leading to the decline of such severe pollution in the capital.
Districts
London's vast urban area is often described using a set of district names, such as Bloomsbury, Mayfair, Wembley and Whitechapel. These are either informal designations, reflect the names of villages that have been absorbed by sprawl, or are superseded administrative units such as parishes or former boroughs.
Such names have remained in use through tradition, each referring to a local area with its own distinctive character, but without current official boundaries. Since 1965 Greater London has been divided into 32 London boroughs in addition to the ancient City of London. he City of London is the main financial district and Canary Wharf has recently developed into a new financial and commercial hub, in the Docklands to the east.
The West End is London's main entertainment and shopping district, attracting tourists.[88] West London includes expensive residential areas where properties can sell for tens of millions of pounds. The average price for properties in Kensington and Chelsea is £894,000 with similar average outlay in most of Central London.
The East End is the area closest to the original Port of London, known for its high immigrant population, as well as for being one of the poorest areas in London. The surrounding East London area saw much of London's early industrial development; now, brownfield sites throughout the area are being redeveloped as part of the Thames Gateway including the London Riverside and Lower Lea Valley, which is being developed into the Olympic Park for the 2012 Olympics.[91]
Architecture
London's buildings are too diverse to be characterised by any particular architectural style, having been built over a long period of time. Notable recent buildings are the 1980s skyscraper Tower 42, the Lloyd's building with services running along the outside of the structure, and the 2004 Swiss Re building, known as the "Gherkin". London's generally low-rise nature makes these skyscrapers and others such as One Canada Square and its neighbours at Canary Wharf and the BT Tower in Fitzrovia very noticeable from a distance.
High-rise development is restricted at certain sites if it would obstruct protected views of St. Paul's Cathedral. Nevertheless, there are plans for more skyscrapers in central London (see Tall buildings in London), including the 72-story "Shard of Glass", which will be one of the tallest buildings in Europe. Older buildings are mainly brick built, most commonly the yellow London stock brick or a warm orange-red variety, often decorated with carvings and white plaster mouldings.
Many grand houses and public buildings, such as the National Gallery, are constructed from Portland stone. Some areas of the city, particularly those just west of the centre, are characterised by white stucco or whitewashed buildings. Few structures pre-date the Great Fire of 1666, except for a few trace Roman remains, the Tower of London and a few scattered Tudor survivors in the City. Wren's late 17th century churches and the financial institutions of the 18th and 19th century such as the Royal Exchange and the Bank of England, to the early 20th century Old Bailey and the 1960s Barbican Estate form part of the varied architectural heritage.
The disused, but soon to be rejuvenated, 1939 Battersea Power Station by the river in the south-west is a local landmark, while some railway termini are excellent examples of Victorian architecture, most notably St Pancras and Paddington.[93] The density of London varies, with high employment density in the central area, high residential densities in inner London and lower densities in the suburbs.
In the dense areas, most of the concentration is achieved with medium- and high-rise buildings. London's skyscrapers such as "Gherkin", Tower 42, the Broadgate Tower and One Canada Square are usually found in the two financial districts, the City of London and Canary Wharf. Other notable modern buildings include City Hall in Southwark with its distinctive oval shape,[94] and the British Library in Somers Town/Kings Cross. What was formerly the Millennium Dome, located by the Thames to the east of Canary Wharf, is now used as an entertainment venue known as The O2.
The Monument in the City of London provides views of the surrounding area while commemorating the Great Fire of London, which originated nearby. Marble Arch and Wellington Arch, at the north and south ends of Park Lane respectively, have royal connections, as do the Albert Memorial and Royal Albert Hall in Kensington. Nelson's Column is a nationally recognised monument in Trafalgar Square, one of the focal points of the centre.
Parks and gardens
The largest parks in the central area of London are the Royal Parks of Hyde Park, its neighbour Kensington Gardens at the western edge of central London and Regent's Park on the northern edge. Regent's Park contains London Zoo, the world's oldest scientific zoo, and is located near the tourist attraction of Madame Tussauds Wax Museum.
Closer to central London are the smaller Royal Parks of Green Park and St. James's Park. Hyde Park in particular is popular for sports and sometimes hosts open-air concerts. A number of large parks lie outside the city centre, including the remaining Royal Parks of Greenwich Park to the sh-east and Bushy Park and Richmond Park to the south-west, as well as Victoria Park, East London to the east. Primrose Hill to the north of Regent's Park is a popular spot to view the city skyline.
Some more informal, semi-natural open spaces also exist, including the 791-acre (3.2 km2) Hampstead Heath of North London. This incorporates Kenwood House, the former stately home and a popular location in the summer months where classical musical concerts are held by the lake, attracting thousands of people every weekend to enjoy the music, scenery and fireworks.
Demography
| Country of Birth[103] | Population
(2001) |
|---|
 United Kingdom United Kingdom | 5,230,155 |
 India India | 172,162 |
 Republic of Ireland Republic of Ireland | 157,285 |
 Bangladesh Bangladesh | 84,565 |
 Jamaica Jamaica | 80,319 |
 Nigeria Nigeria | 68,907 |
 Pakistan Pakistan | 66,658 |
 Kenya Kenya | 66,311 |
 Sri Lanka Sri Lanka | 49,932 |
 Ghana Ghana | 46,513 |
 Cyprus Cyprus | 45,888 |
 South Africa South Africa | 45,506 |
 United States United States | 44,622 |
 Australia Australia | 41,488 |
 Germany Germany | 39,818 |
 Turkey Turkey | 39,128 |
 Italy Italy | 38,694 |
 France France | 38,130 |
 Somalia Somalia | 33,831 |
 Uganda Uganda | 32,082 |
 New Zealand New Zealand | 27,494 |
With increasing industrialisation, London's population grew rapidly throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries, and it was for some time in the late 19th and early 20th centuries the most populous city in the world until overtaken by New York in 1925. Its population peaked at 8,615,245 in 1939 immediately before the outbreak of World War 2. There were an estimated 7,556,900 official residents in Greater London as of mid-2007.
However, London's continuous urban area extends beyond the borders of Greater London and was home to 8,278,251 people in 2001,[2] while its wider metropolitan area has a population of between 12 and 14 million depending on the definition used.[104] According to Eurostat, London is the most populous city and metropolitan area of the European Union and the second most populous in Europe (or third if Istanbul is included). During the period 1991–2001 a net 726,000 immigrants arrived in London.
The region covers an area of 609 square miles (1,580 km2). The population density is 12,331 inhabitants per square mile (4,761 /km2), more than ten times that of any other British region. In terms of population, London is the 25th largest city and the 18th largest metropolitan region in the world. It is also ranked 4th in the world in number of billionaires (United States Dollars) residing in the city. London ranks as one of the most expensive cities in the world, alongside Tokyo and Moscow.
Ethnic groups
According to the Office for National Statistics, based on 2006 estimates, 69.4 per cent of the 7.5 million inhabitants of London were White, with 58 per cent White British, 2.5 per cent White Irish and 8.9 per cent classified as Other White. Some 13.1 per cent are of South Asian descent, with Indians making up 6.5 per cent of London's population, followed by Bangladeshis and Pakistanis at 2.3 per cent each. 2 per cent are categorised as "Other Asian".
10.7 per cent of London's population are Black, with around 5.5 per cent being Black African, 4.3 per cent as Black Caribbean and 0.7 per cent as "Other Black". 3.5 per cent of Londoners are of mixed race; 1.5 per cent are Chinese; and 1.9 per cent belong to another ethnic group.[5] As of 2008, 40% of London's total population was from an ethnic minority group.
Across London, Black and Asian children outnumber White British children by about six to four. In January 2005, a survey of London's ethnic and religious diversity claimed that there were more than 300 languages spoken and more than 50 non-indigenous communities which have a population of more than 10,000 in London. Figures from the Office for National Statistics show that, as of 2006, London's foreign-born population is 2,288,000 (31%), up from 1,630,000 in 1997.
The 2001 census showed that 27.1% of Greater London's population were born outside the UK, and a slightly higher proportion were classed as non-white. The table to the right shows the 'Country of Birth' of London residents in 2001, the date of the last UK Census. (Top 21). A portion of the German-born population are likely to be British nationals o parents serving in the British Armed Forces in Germany.
Religion
The majority of Londoners – 58.2% – identify themselves as Christians.[115] This is followed by those of no religion (15.8%), Muslims (8.5%), Hindus (4.1%), Jews (2.1%), Sikhs (1.5%), Buddhists (0.8%), Pagans/Wiccans (0.3%) and other (0.2%), though 8.7% of people did not answer this question in the 2001 Census.[115]
London has traditionally been dominated by Christianity, and has a large number of churches, particularly in the City of London. The well-known St Paul's Cathedral in the City and Southwark Cathedral south of the river are Anglican administrative centres, while the Archbishop of Canterbury, principal bishop of the Church of England and worldwide Anglican Communion, has his main residence at Lambeth Palace in the London Borough of Lambeth.
Important national and royal ceremonies are shared between St Paul's and Westminster Abbey. The Abbey is not to be confused with nearby Westminster Cathedral, which is the largest Roman Catholic cathedral in England and Wales.[119] Despite the prevalence of Anglican churches, observance is very low within the Anglican denomination. Church attendance continues on a long, slow, steady decline, according to Church of England statistics.
London is also home to sizeable Muslim, Hindu, Sikh, and Jewish communities. Many Muslims live in Tower Hamlets and Newham; the most important Muslim edifice is London Central Mosque on the edge of Regent's Park. Following the oil boom, increasing numbers of wealthy Middle-Eastern Muslims have based themselves around Mayfair and Knightsbridge in West London.
London's large Hindu community is found in the north-western boroughs of Harrow and Brent, the latter of which is home to one of Europe's largest Hindu temples, Neasden Temple. Sikh communities are located in East and West London, which is also home to the largest Sikh temple in the world outside India.
The majority of British Jews live in London, with significant Jewish communities in Stamford Hill, Stanmore, Golders Green, Hampstead,[126] Hendon, and Edgware in North London. Stanmore and Canons Park Synagogue has the largest membership of any single Orthodox synagogue in the whole of Europe, overtaking Ilford synagogue (also in London) in 1998. The community set up the London Jewish Forum in 2007 in response to the growing significance of devolved London Government.
Economy
London is a major centre for international business and commerce and is one of three "command centres" for the world economy, with New York City and Tokyo. According to 2005 estimates by the PricewaterhouseCoopers accounting firm, London has the 6th largest city economy in the world after Tokyo, New York City, Los Angeles, Chicago, and Paris.
London generates approximately 20% of the UK's GDP[13] (or $446 billion in 2005); while the economy of the London metropolitan area—the second largest in Europe—generates approximately 30% of the UK's GDP (or an estimated $669 billion in 2005). London is one of the pre-eminent financial centres of the world and vies with New York City as the most important location for international finance.
London's largest industry is finance, and its financial exports make it a large contributor to the UK's balance of payments. Around 325,000 people were employed in financial services in London until mid-2007. London has over 480 overseas banks, more than any other city in the world. Due to its prominent global role, London's economy has been affected by the global financial crisis of 2008–2009. The City of London estimates that 70,000 jobs in finance will be cut within a year.[135]

Canary Wharf is the home of the United Kingdom's tallest building
More than half of the UK's top 100 listed companies (the FTSE 100) and over 100 of Europe's 500 largest companies are headquartered in central London. Over 70% of the FTSE 100 are located within London's metropolitan area, and 75% of Fortune 500 companies have offices in London.[136] The City of London is home to the Bank of England, London Stock Exchange, and Lloyds of London insurance market. Along with professional services, media companies are concentrated in London and the media distribution industry is London's second most competitive sector.[137] The BBC is a significant employer, while other broadcasters also have headquarters around the city. Many national newspapers are edited in London.
Tourism is one of London's prime industries and employs the equivalent of 350,000 full-time workers in London in 2003,[138] while annual expenditure by tourists is around £15 billion.[139] A study carried out by Euromonitor in October 2007 places London at first place out of 150 of the world's most popular cities, attracting 15.6 million international tourists in 2006.[140] London attracts 27 million overnight-stay visitors every year.[141] The Port of London is the second-largest in the United Kingdom, handling 53 million tonnes of cargo each year.[142]
Transport

The
London Underground, oldest and largest metro system in the world,
[143] known as the The Tube, because of the shape of the tunnels
Transport is one of the four main areas of policy administered by the Mayor of London,[144] however the mayor's financial control does not extend to the longer distance rail network that enters London. In 2007 he assumed responsibility for some local lines, which now form the London Overground network, adding to the existing responsibility for the London Underground, trams and buses. The public transport network is administered by Transport for London (TfL) and is one of the most extensive in the world. Cycling is an increasingly popular way to get around London. The London Cycling Campaign lobbies for better provision.[145]
The lines that formed the London Underground, as well as trams and buses, became part of an integrated transport system in 1933 when the London Passenger Transport Board (LPTB) or London Transport was created. Transport for London (TfL), is now the statutory corporation responsible for most aspects of the transport system in Greater London, and is run by a board and a commissioner appointed by the Mayor of London.[146]
[edit] Railways
The London Underground — all of which is now commonly referred to as The Tube, though originally this designation referred only to the deep-level lines, as distinct from the sub-surface lines — is one of the oldest, longest, and most expansive metro systems in the world, dating from 1863.[21][147] The system serves 270 stations[148] and was formed from several private companies, including the world's first underground electric line, the City and South London Railway.[149]
Over three million journeys a day are made on the Underground network, over 1 billion journeys each year.[150][151] An investment programme is attempting to address congestion and reliability problems, including £7 billion (€10 billion) of improvements planned for the Olympics.[152] London has been commended as the city with the best public transport.[153] The Docklands Light Railway is a second, more local metro system using smaller and lighter tram-type vehicles, which opened in 1987, serving Docklands and Greenwich.
There is an extensive above-ground suburban railway network, particularly in South London, which has fewer Underground lines. London houses Britain's busiest station - Waterloo with over 177 millon people using the interchange station each year which has services to South West London and parts of southern and western England.[154][155] Most rail lines terminate around the centre of London, running into fourteen terminal stations with the exception of the Thameslink trains connecting Bedford in the north and Brighton in the south via Luton and Gatwick Airports.[156]
Since 2007 High-speed Eurostar trains link St Pancras International with Lille, Paris, and Brussels. Journey times to Paris and Brussels of 2h 15 and 1h 51 respectively make London closer to continental Europe than the rest of Britain by virtue of the High Speed 1 rail link to the Channel Tunnel[157] while the first high speed domestic trains started in June 2009 linking Kent to London.[158]
[edit] Buses and trams
London's bus network is one of the largest in the world, running 24 hours a day, with 8,000 buses, 700 bus routes, and over 6 million passenger journeys made every weekday. In 2003, the network's ridership was estimated at over 1.5 billion passenger trips per annum, more than the Underground.[159] Around £850 million is taken in revenue each year. London has the largest wheelchair accessible network in the world[160] and, from the 3rd quarter of 2007, became more accessible to hearing and visually impaired passengers as audio-visual announcements were introduced. The distinctive red double-decker buses are internationally recognised, and are a trademark of London transport along with black cabs and the Tube.[161][162]
London has a modern tram network, known as Tramlink, based around Croydon in South London. The network has 39 stops, 3 routes and carried 26.5 million people in 2008. Since June 2008 Transport for London has completely owned tramlink and plans to spend £54m until 2015 on maintenance, renewals, upgrades and capacity enhancements. Since April 2009 all trams have now been refurbished.[163]
London is a major international air transport hub with the largest city airspace in the world. Eight airports use the word London in their name, but most traffic passes through only five. London Heathrow Airport, in Hillingdon, West London, is the busiest airport in the world for international traffic, and is the major hub of the nation's flag carrier, British Airways.[165] In March 2008 its fifth terminal was opened,[166] and plans are already being considered for a sixth terminal[167] and third runway. Similar traffic, with the addition of some low-cost short-haul flights, is also handled at London Gatwick Airport, located south of London in West Sussex.[168]
London Stansted Airport, situated north east of London in Essex, is the main hub for Ryanair, and London Luton Airport to the north of London in Bedfordshire, caters mostly for low-cost short-haul flights.[169][170] London City Airport, the smallest and most central airport, is focused on business travellers, with a mixture of full service short-haul scheduled flights and considerable business jet traffic.[171]
Although the majority of journeys involving central London are made by public transport, car travel is common in the suburbs. The inner ring road (around the city centre), the North and South Circular roads (in the suburbs), and the outer orbital motorway (the M25, outside the built-up area) encircle the city and are intersected by a number of busy radial routes—but very few motorways penetrate into inner London. The M25 is the longest ring-road motorway in the world at 121.5 miles (195.5 km) long.[172]
A plan for a comprehensive network of motorways throughout the city (the Ringways Plan) was prepared in the 1960s but was mostly cancelled in the early 1970s. In 2003, a congestion charge was introduced to reduce traffic volumes in the city centre. With a few exceptions, motorists are required to pay £8 per day to drive within a defined zone encompassing much of congested central London.[173][174] Motorists who are residents of the defined zone can buy a vastly reduced season pass which is renewed monthly and is cheaper than a corresponding bus fare.[175] London is notorious for its traffic congestion, with the M25 motorway the busiest stretch in the country. The average speed of a car in the rush hour is 10.6 mph.[176]
Education
Home to a range of universities, colleges and schools, London has a student population of about 378,000 and is a centre of research and development. Most primary and secondary schools in London follow the same system as the rest of England—comprehensive schooling. With 125,000 students, the University of London is the largest contact teaching university in the United Kingdom and in Europe.[177] It comprises 20 colleges as well as several smaller institutes each with a high degree of autonomy.
Constituent colleges have their own admissions procedures, and are effectively universities in their own right, although most degrees are awarded by the University of London rather than the individual colleges. Its constituents include multi-disciplinary colleges such as Royal Holloway, Birkbeck, UCL,[178] King's, Goldsmiths, Queen Mary[179] and more specialised institutions such as the London School of Economics,[180] SOAS,[181] the Royal Academy of Music, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine,[182] the Courtauld Institute of Art and the Institute of Education.[183]
University College London and Imperial College London have been ranked among the top ten universities in the world by Times Higher Education: in 2009 UCL was ranked the 4th best and Imperial the 5th best university in the world.[184] In addition, the London School of Economics has been described as the world‘s leading social science institution for teaching and research, and has the most international student body of any university in the world today.[185]
A number of colleges are dedicated to the fine arts, including the Royal College of Music, Royal College of Art, and Guildhall School of Music and Drama. London's other universities, such as Brunel University, City University, London Metropolitan University, Middlesex University, University of East London, University of the Arts London, University of Westminster, Kingston University and London South Bank University are not part of the University of London but are still leaders in their field and popular choices among students both nationally and internationally. Some were polytechnics until they were granted university status in 1992, and others which were founded much earlier. Imperial College London left the federal University of London in 2007.
Since the merger of University of North London and London Guildhall University in 2003, London Metropolitan University is the largest unitary university in the capital, with over 34,000 students from 155 countries.[186] London is also known globally for its business education, harbouring several top-rated business schools: London Business School, Cass Business School and Imperial College Business School [187] In addition there are three international universities: Schiller International University, Richmond University and Regent's College.
 of the Malay Peninsula, 137 kilometres (85 mi) north of the equator, south of the Malaysian state of Johor and north of Indonesia's Riau Islands. At 710.2 km2 (274.2 sq mi), Singapore is a microstate and the smallest nation in Southeast Asia. It is substantially larger than Monaco and Vatican City, the only other surviving sovereign city-states.
of the Malay Peninsula, 137 kilometres (85 mi) north of the equator, south of the Malaysian state of Johor and north of Indonesia's Riau Islands. At 710.2 km2 (274.2 sq mi), Singapore is a microstate and the smallest nation in Southeast Asia. It is substantially larger than Monaco and Vatican City, the only other surviving sovereign city-states.